Industrial Networking Solutions: What Are The Most Common Solutions And How Is HD-PLC Superior To Them?

The global industrial networking solutions market is projected to reach $23.84 Billion by 2022.
This very competitive market is largely dominated by wired networking solutions, such as Fieldbus and Industrial Ethernet.
And while there are reasons why these solutions are so prominent in the market, they are not without their limitations.
As a result, HD-PLC has emerged as a promising solution that helps resolve some of the challenges that other types of industrial networks present.
In this blog post, we will:
- Explore the most popular industrial networking solutions
- List their advantages and disadvantages
- Highlight the aspects in which HD-PLC is superior to other solutions
What Are The Most Popular Industrial Networking Solutions?
Research conducted by HMS Industrial Networks suggests the following market shares and dynamic of the most popular industrial networking solutions:
- Industrial Ethernet — 64%. Industrial Ethernet, an application of the Ethernet protocol in industrial settings with a focus on real-time control, is the most popular industrial networking solution. It occupies over a half of the market, with EtherNet/IP being the most widespread protocol at a 17% market share. Industrial Ethernet’s market share has grown considerably over the last decade, from 29% in 2014, and its growth remains strong.
- Fieldbus — 30%. Fieldbus is a family of industrial networking solutions, defined by the IEC 61158 Even though Fieldbus was the dominant solution in the market for quite some time, its market share has weakened considerably in the last few years, falling from 71% in 2014. Still, it remains an important standard for the industry, with PROFIBUS being the most widespread profile.
- Wireless — 6%. Industrial applications of Wireless solutions, such as WLAN or Bluetooth, have only started appearing recently. However, they are still rather limited with a market share of only 6%.
Fieldbus: Advantages And Disadvantages
Fieldbus is an umbrella term for a range of industrial networking solutions designed for real-time distributed control.
It is most used in the manufacturing industry — for instance, to connect equipment and tools.
The first commercially available Fieldbus solution was Bitbus, created by Intel Corporation in the early 1980s. However, it is hardly widespread anymore, with the most popular solution on the market being the Siemens-made PROFIBUS.
Apart from manufacturing applications, Fieldbus solutions, such as LON, are also found in process and building automation.
Fieldbus Advantages
- Durability: As a communication standard developed specifically for industrial applications, Fieldbus cables and components are designed to be especially durable, robust and capable to withstand extreme physical conditions.
- Reliability: Fieldbus networks use short signal paths and boast increased interference protection, improving network stability and reliability.
- Uniformity: Most Fieldbus solutions have been around for quite a while and are standardized, making it easy to implement equipment from various manufacturers in one system.
Fieldbus Disadvantages
- High equipment cost: While the labor costs of installing a Fieldbus network are quite low, the actual network equipment and components are quite expensive.
- Low data transmission rates: Most Fieldbus solutions operate at data transmission rates of hundreds of kilobytes per second, with only a few standards that can reach speeds of over 10 Mbps.
- High complexity: Fieldbus networks rely heavily on complex proprietary manufacturer equipment. As such, they require professionals who specialize in such equipment in order to be built and maintained.

Wireless As An Industrial Network Solution: Advantages And Disadvantages
Industrial Wireless networking solutions is a sophisticated term for Wireless communication technology, which millions of people worldwide use in their everyday lives.
Implementing Wireless technology in industrial networking settings centers around the familiar solutions, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and LTE.
The only difference between industrial Wireless and commercial or home-use Wireless solutions is that the hardware and protocols of the former are modified to accommodate more sophisticated network topologies and the use cases of industrial networks.
Just like other solutions, Wireless comes with a set of advantages and disadvantages in industrial use cases.
Wireless Advantages
- Flexibility: Adding a new device or piece of equipment to a Wireless network does not require additional wiring or lengthy planning, making network management relatively easy and efficient.
- Scalability: A Wireless network can easily be extended to cover longer distances through repeaters that are a lot less time-consuming to install than wiring.
- Repairability: A Wireless network includes a lot less physical equipment than a wired network. As such, whenever a failure occurs in such a network, it usually concerns one of the few pieces of hardware or software, making it much easier to diagnose, resolve and prevent network issues.
Wireless Disadvantages
- Unstable connection: The performance of wireless networks becomes unstable due to environmental noise and/or changes in the propagation path caused by the movement of people and objects.
- High network expansion cost: Wireless networking equipment is not cheap to begin with. However, the overall network costs can increase even further if the network needs to be expanded to cover a wider area.
- Diminishing connection quality over long distances: While Wireless networks can provide data rates of tens of Mbps, this can only be achieved if the connected equipment stays in relative proximity to the signal source. The further the equipment is from the source, the slower the connection will be — unless the costly range extension equipment is implemented.
Industrial Ethernet: Advantages And Disadvantages
Industrial Ethernet is based on the same IEEE 802.3 standard as Ethernet networks, found in commercial and home environments.
However, it operates under specific protocols, designed to satisfy the requirements of industrial networking applications — such as EtherNet/IP, PROFINET and EtherCAT.
The operating principle of these protocols is focused on providing low-latency or real-time data transmission, courtesy of a modified MAC (Media Access Control) layer.
Another distinctive quality of Industrial Ethernet is the increased ruggedness of the physical equipment, such as switches and cables, that often must reliably operate in extreme conditions.
Ethernet is, by far, the most prominent industrial networking solution — largely thanks to the advantages outlined below. However, it does have a set of disadvantages as well.
Industrial Ethernet Advantages
- Interoperability and familiarity: All Industrial Ethernet protocols are not only interoperable with each other, but also with other Ethernet standards. Moreover, all these solutions can be implemented with the widely available twisted pair cables and protocol converters, making the necessary hardware easy to procure and replace if necessary.
- High connection speed: Ethernet can achieve data transmission rates of up to 1 Gbps, offering performance that is difficult to achieve with other solutions.
- Stability: Ethernet is renowned for its ability to provide a high-speed, stable connection that can support even the most demanding applications.
Industrial Ethernet Disadvantages
- Excessive cost: Ethernet networks among the costliest industrial networking solutions on the market and are not necessarily capable of providing a reasonable return on investment.
- High complexity: Ethernet networks require more equipment and cabling than other industrial networking solutions to function well in an industrial setting, resulting in more complex infrastructures that can be time-consuming and labor-intensive to maintain.
- High barriers to entry for some solutions: Some of the most popular Industrial Ethernet solutions, such as EtherNet/IP can only be implemented after obtaining a costly license and proprietary specifications from ODVA — the vendor behind the technology. By contrast, most Fieldbus solutions, such as MODBUS, are open-source and can implemented without licensing and approval from any organization.

Why Is HD-PLC Superior To Other Industrial Network Solutions?
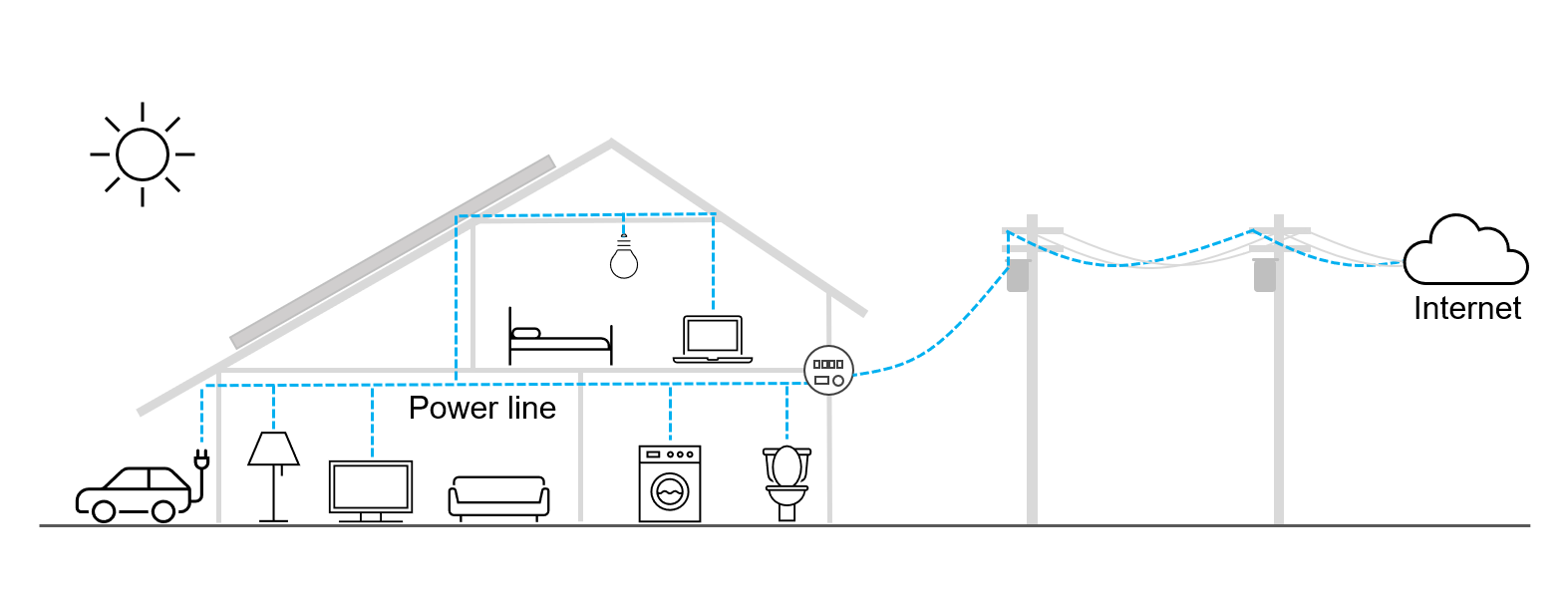
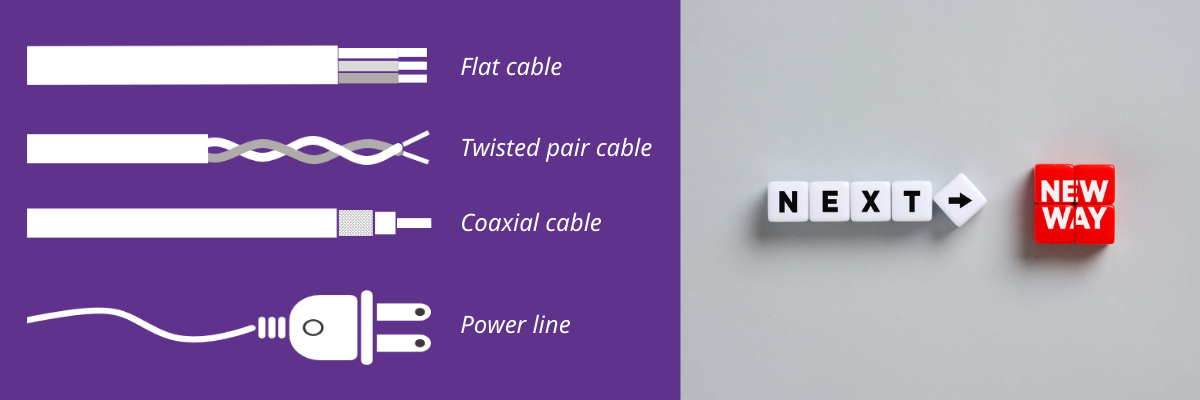
The key concept behind HD-PLC is transferring data over existing cabling, whatever this cabling may be: power lines, twisted pair cables, coaxial cables and so on.
As such, HD-PLC’s main strengths as an industrial networking solution come from the fact that it combines some of the benefits of other technologies while alleviating some of their challenges.
Here’s how HD-PLC compares to Fieldbus, Wireless and Industrial Ethernet solutions across some of the main network characteristics:
- Speed: HD-PLC can reach a maximum theoretical PHY layer speed of 240Mbps and tens of Mbps in most practical applications. This places HD-PLC on par with real-life implementations of Wireless, ahead of Fieldbus solutions, yet behind Industrial Ethernet.
- Reliability: One of HD-PLC’s key innovations is the unique Wavelet-OFDM modulation method that helps reduce data loss and interference, significantly improving not only the data transmission rate, but also signal stability. HD-PLC networks can also be built using existing wiring, which can help resolve the reliability concerns that come with building a brand-new communication infrastructure.
- Complexity: Because HD-PLC networks do not require installation of additional wiring and the hardware components involved are quite limited, the overall network complexity is quite low compared to Industrial Ethernet or Fieldbus networks.
- Range: Another unique feature of HD-PLC is the Multi-hop technology that can act as a range extension tool. HD-PLC Multi-hop networks can provide a stable connection with as many as 1,024 individual nodes and span distances of several kilometers.
- Cost: The strongest advantage that HD-PLC has over other industrial networking solutions is its cost effectiveness. HD-PLC does not require additional investment into wiring in most cases, and other physical network components are a lot less expensive compared to Ethernet or Fieldbus solutions. As such, HD-PLC boasts a very strong ROI for the market.
HD-PLC is a solution that is best for customers who desire more performance than Fieldbus can provide but cannot introduce Ethernet due to the high installation cost.
While in some cases, Ethernet can still have an edge over HD-PLC in terms of connection speed and network stability, this edge is not always justified considering Ethernet’s high costs.
HD-PLC can provide the best of both worlds in terms of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Ready to build your own HD-PLC network?
HD-PLC As An Industrial Networking Solution — Takeaways
The industrial networking solutions market keeps growing larger and more competitive, as the demand for automation solutions increases.
Despite the competitiveness, it has been dominated by three main solutions: Fieldbus, Wireless and Industrial Ethernet.
And while these solutions have prominent market positions, each comes with a set of advantages and disadvantages:
- Fieldbus is a widely recognized solution that is easy to install and operate, yet it’s costly, complex and offer a low data rate
- Wireless solutions provide great network flexibility and relatively hassle-free maintenance but can suffer from poor range and connectivity issues.
- Industrial Ethernet is a versatile, familiar, high-performance solution, the cost and complexity of which can be prohibitive.
By comparison to these solutions, HD-PLC is a cost-effective, efficient and reliable networking solution that offers some of the same benefits as other solutions — albeit, at a lower cost.